Admiralty Brass
- Home
- >
- Condenser Tubes
- >
- Admiralty Brass
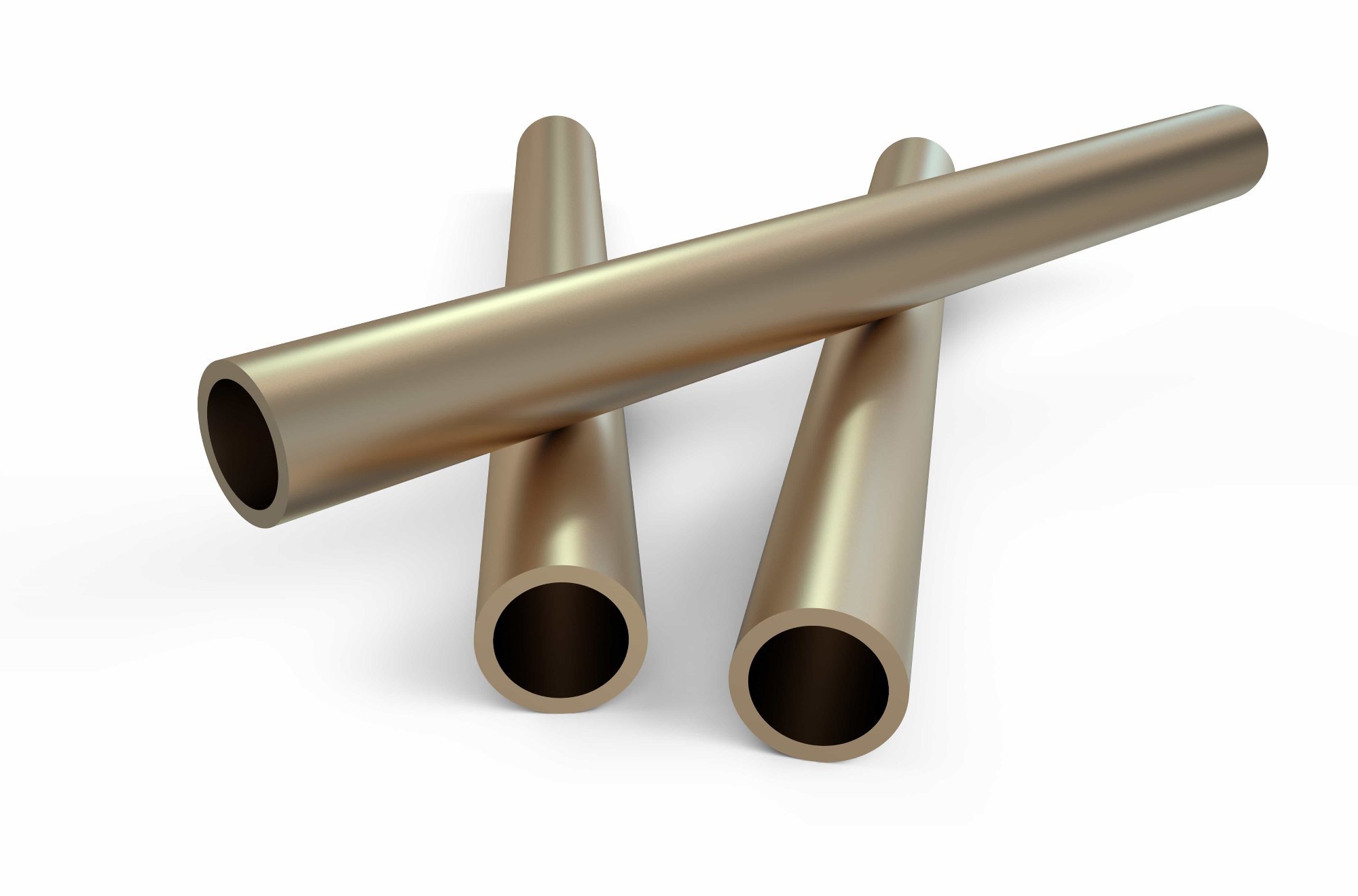

Admiralty Brass
Admiralty brass is a type of brass alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, especially in seawater, making it particularly suitable for marine applications. Here are the key details about Admiralty brass:
Composition:
Admiralty brass typically consists of:
- Copper (Cu): Approximately 70-73%
- Zinc (Zn): Approximately 27-30%
- Trace amounts of other elements such as iron (Fe), lead (Pb), tin (Sn), and arsenic (As).
Grades
ASTM B 111 C 44300 / ASME SB 111 C 44300:
- ASTM B 111: Standard specification for copper and copper-alloy seamless condenser tubes and ferrule stock.
- ASME SB 111: Identical to ASTM B 111, but used in ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications.
BS 2871 Part 3 CZ-111:
- BS 2871: British Standard specification for copper and copper alloys. Part 3 covers wrought and cast high conductivity copper alloys for electrical purposes.
- CZ-111: Specifically refers to Admiralty brass within the British Standard system.
EN 12451 CuZn28:
- EN 12451: European Standard for copper and copper alloys. CuZn28 specifically denotes Admiralty brass (Cu 71-73%, Zn 27-29%).
SniAs - CW 706B:
- SniAs: Often refers to the Indonesian National Standard for Admiralty brass.
- CW 706B: Classification according to the British Standard system for copper alloys.
51 102 / CuZn29Sn1:
- 51 102: Identification number for Admiralty brass alloys.
- CuZn29Sn1: Another designation for Admiralty brass, specifying its composition (Cu 70-72%, Zn 28-30%, Sn 0.9-1.2%).
JIS H C 4430:
- JIS: Japanese Industrial Standard.
- H C 4430: Japanese standard designation for Admiralty brass.
Properties:
Corrosion Resistance: Admiralty brass exhibits exceptional resistance to corrosion, particularly in marine environments where seawater exposure is common. This is due to the alloy’s high copper content.
Strength: It has good strength, which is advantageous for structural applications.
Machinability: Admiralty brass is relatively easy to machine and work with, which enhances its utility in manufacturing processes.
Weldability: It is weldable using standard techniques, which allows for ease of fabrication.
Heat Conductivity: Like other brass alloys, Admiralty brass has good thermal conductivity, making it useful in heat exchanger applications.
Applications:
Marine Equipment: Admiralty brass is widely used in the marine industry for components like condenser tubes, heat exchanger tubes, fittings, and fasteners.
Heat Exchangers: Its corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity make it ideal for heat exchanger tubes in industrial applications.
Plumbing: Used in plumbing fittings and fixtures due to its corrosion resistance and durability.
Automotive: In some cases, Admiralty brass is used in automotive radiators and heater cores.
Other Products
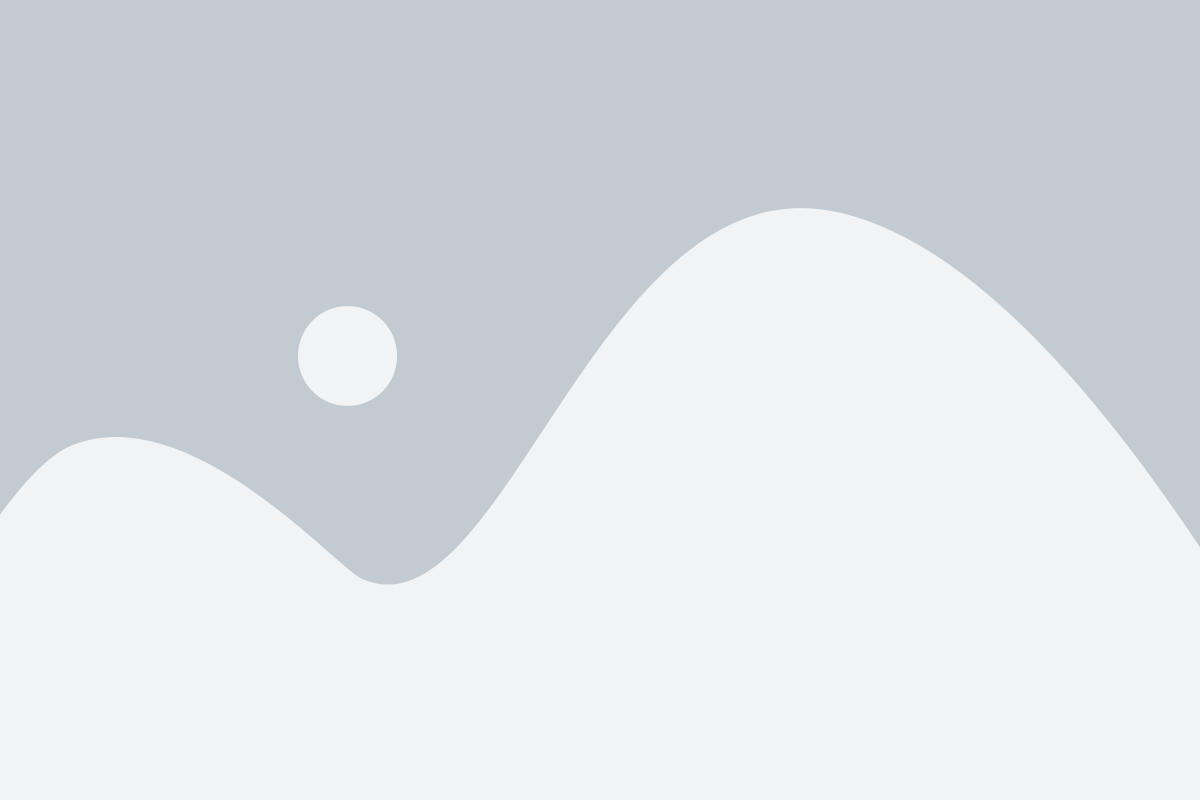

Admiralty Brass
Admiralty brass is a type of brass alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, especially in seawater, making it particularly suitable for marine applications. Here are the key details about Admiralty brass:
Composition:
Admiralty brass typically consists of:
- Copper (Cu): Approximately 70-73%
- Zinc (Zn): Approximately 27-30%
- Trace amounts of other elements such as iron (Fe), lead (Pb), tin (Sn), and arsenic (As).
Properties:
Corrosion Resistance: Admiralty brass exhibits exceptional resistance to corrosion, particularly in marine environments where seawater exposure is common. This is due to the alloy’s high copper content.
Strength: It has good strength, which is advantageous for structural applications.
Machinability: Admiralty brass is relatively easy to machine and work with, which enhances its utility in manufacturing processes.
Weldability: It is weldable using standard techniques, which allows for ease of fabrication.
Heat Conductivity: Like other brass alloys, Admiralty brass has good thermal conductivity, making it useful in heat exchanger applications.
Applications:
Marine Equipment: Admiralty brass is widely used in the marine industry for components like condenser tubes, heat exchanger tubes, fittings, and fasteners.
Heat Exchangers: Its corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity make it ideal for heat exchanger tubes in industrial applications.
Plumbing: Used in plumbing fittings and fixtures due to its corrosion resistance and durability.
Automotive: In some cases, Admiralty brass is used in automotive radiators and heater cores.
ASTM B 111 C 44300 / ASME SB 111 C 44300:
- ASTM B 111: Standard specification for copper and copper-alloy seamless condenser tubes and ferrule stock.
- ASME SB 111: Identical to ASTM B 111, but used in ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications.
BS 2871 Part 3 CZ-111:
- BS 2871: British Standard specification for copper and copper alloys. Part 3 covers wrought and cast high conductivity copper alloys for electrical purposes.
- CZ-111: Specifically refers to Admiralty brass within the British Standard system.
EN 12451 CuZn28:
- EN 12451: European Standard for copper and copper alloys. CuZn28 specifically denotes Admiralty brass (Cu 71-73%, Zn 27-29%).
SniAs - CW 706B:
- SniAs: Often refers to the Indonesian National Standard for Admiralty brass.
- CW 706B: Classification according to the British Standard system for copper alloys.
51 102 / CuZn29Sn1:
- 51 102: Identification number for Admiralty brass alloys.
- CuZn29Sn1: Another designation for Admiralty brass, specifying its composition (Cu 70-72%, Zn 28-30%, Sn 0.9-1.2%).
JIS H C 4430:
- JIS: Japanese Industrial Standard.
- H C 4430: Japanese standard designation for Admiralty brass.
